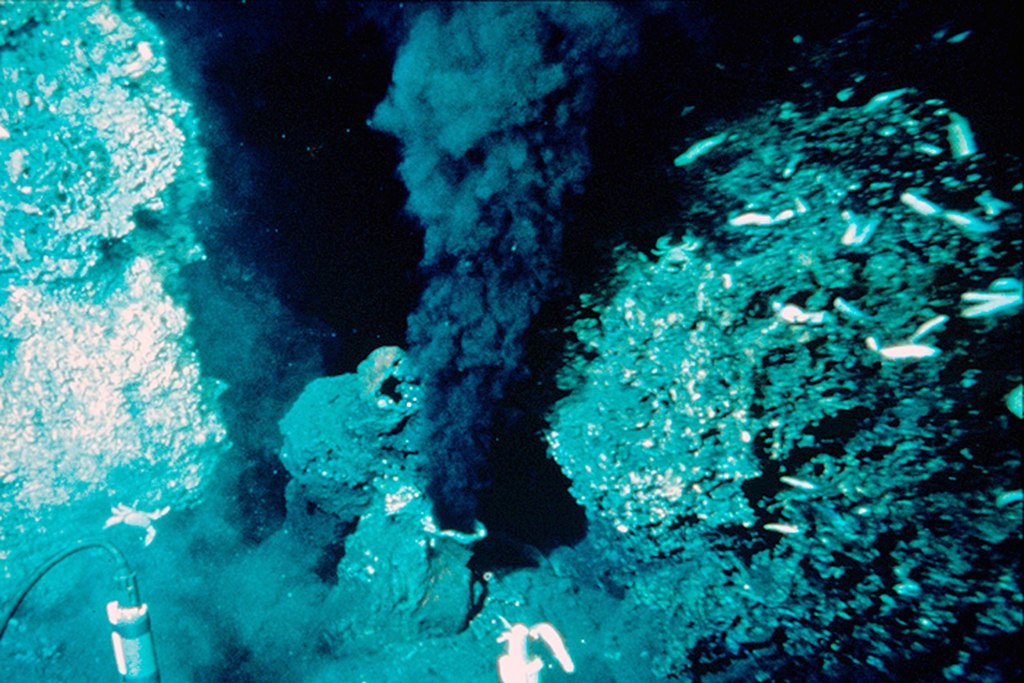
Submarine metalliferous carbonate mounds in the Cambrian of the Baltoscandian Basin induced by vent networks and water column stratification (ÁLVARO et al., 2022)
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-12379-y
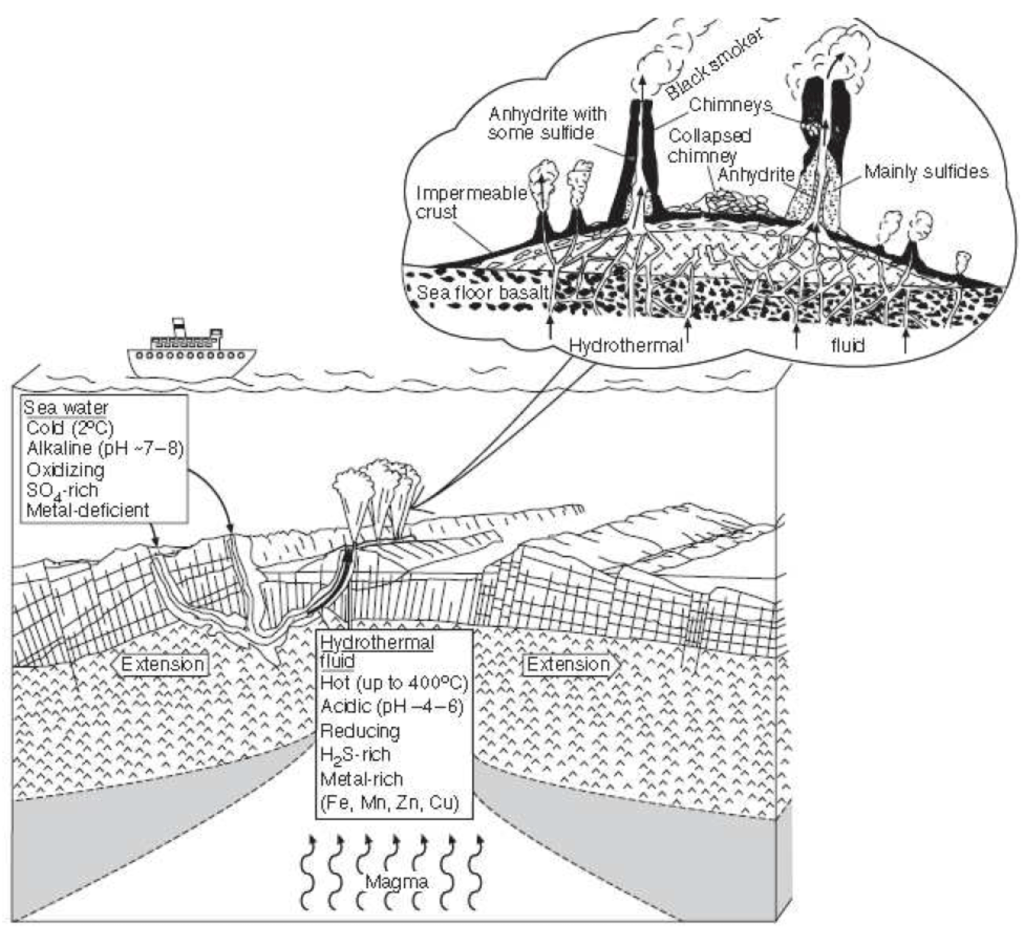
Geological, physical, and chemical characteristics of seafloor hydrothermal vent fields (ZHENG et al., 2020)
MARHYS (MARine HYdrothermal Solutions) Database: A Global Compilation of Marine Hydrothermal Vent Fluid, End Member, and Seawater Compositions (DIEHL and BACH, 2020)
https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2020GC009385
MARHYS Database, Version 2.0 (DIEHL and BACH, 2021)
https://doi.pangaea.de/10.1594/PANGAEA.935649
Also…
Sea level stability over geologic time owing to limited deep subduction of hydrous mantle (CERPA et al., 2022)
https://eartharxiv.org/repository/view/1958/